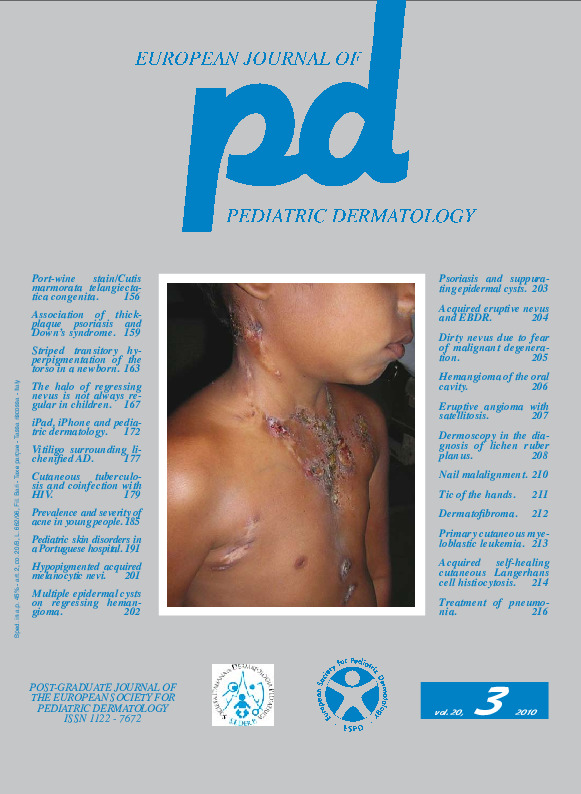
Cutaneous tuberculosis and coinfection with HIV in Indian children.
Downloads
How to Cite
Anupam V., Tarang G. 2010. Cutaneous tuberculosis and coinfection with HIV in Indian children. Eur. J. Pediat. Dermatol. 20 (3):179-84.
pp. 179-84
Abstract
Although many studies have been done worldwide stating the incidence of tuberculosis developing in children with HIV, very few are available which state the overall incidence of HIV seen in pediatric age group having tuberculosis with changes in presentation of the same due to immunosuppression. This study is aimed at reporting various clinical forms of childhood cutaneous tuberculosis and HIV concurrence rates in children seen during the last 3 years in a tertiary care hospital of North India. Patients with cutaneous tuberculosis in Dermatology Outpatient Department of our institute from October 2006 to September 2009 were considered. Criteria for diagnosis were clinical and histopathological, besides microbiological tests for tuberculosis and HIV. Despite efforts, we could not find studies stating incidence of paediatric HIV co-infection with respect to pediatric tubercular infection. All we gathered was incidence of tuberculosis developing in HIV infected children. Out of total 76 cases with cutaneous tuberculosis in the pediatric age group, incidence of HIV concurrence was reported in 27 cases (35.5%). The most common variants seen were scrofuloderma 32 cases (42.1%), lupus vulgaris 17 cases (22.3%), tuberculosis verruca cutis 15 cases (19.7%), lichen scrofulosorum 5 cases (6.5%), disseminated tuberculosis 3 cases (3.9%), metastatic tubercular abcesses 2 cases (2.6%) and papulonecrotic tuberculids 2 cases (2.6%). In view of the varied clinical presentation, physician awareness and high index of suspicion is necessary to diagnose cutaneous forms of tuberculosis and when some atypical presentations are seen, biopsy and monitoring for HIV should be done with prompt follow up.Keywords
Cutaneous tuberculosis, HIV, Scrofuloderma, Lupus vulgaris, Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis, Disseminated miliary tuberculosis, Iatrogenic immunisation tuberculosis, Tubercular gumma