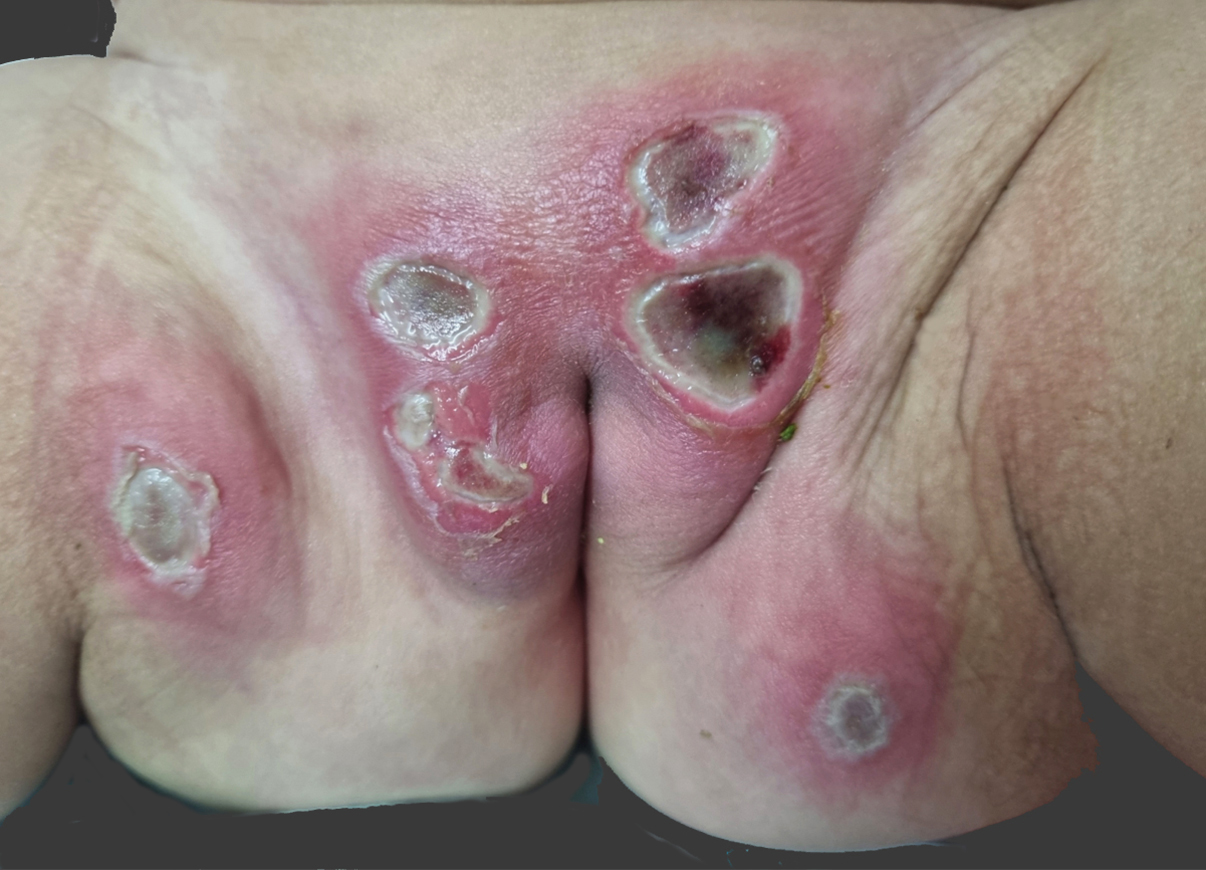
Genital ulcerated nodules revealing primary Epstein-Barr virus infection.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.35.2.2769How to Cite
Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a ubiquitous herpesvirus that infects more than 90% of adults worldwide. While primary EBV infection is often asymptomatic in children, cutaneous manifestations can occur; however, genital lesions remain rare.
A 1-year-old infant presented with a sudden painful ulcerated genital nodules, fever, and diarrhea. Clinical examination showed erythematous necrotic nodules, cervical lymphadenopathy, erythematous angina, and splenomegaly. EBV serology confirmed a primary infection. Treatment with antibiotics and symptomatic care led to complete recovery in three weeks.
This case highlights an unusual presentation of primary EBV infection with ulcerated genital nodules without mucosal involvement, distinct from the more commonly reported Lipschütz ulcer. Further research is needed to understand the pathophysiology of mucocutaneous EBV manifestations.
