BCGitis in a child with common variable immunodeficiency complicated by autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.35.1.2726How to Cite
Abstract
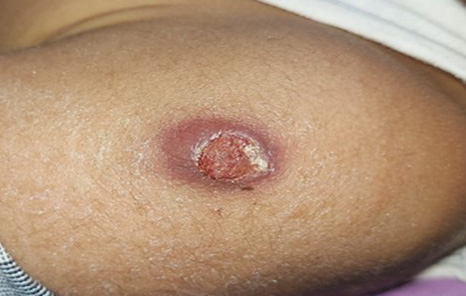
BCGitis is an infection that can occur after vaccination with Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG), which is commonly administered in India to all infants at birth to prevent tuberculosis. We report a case of a 6-year-old boy with common variable immunodeficiency complicated by autoimmune hemolytic anemia, under treatment with immunosuppressants, who presented with a small painful nodule with pus discharge laterally on the left arm with ipsilateral lymphadenopathy. Histopathology and nucleic acid amplification testing confirmed localized BCGitis. Complete resolution of the lesion occurred after 6 months of fixed-dose combination antituberculosis treatment. Therefore, early recognition and treatment of BCGitis in immunocompromised children can have a significant impact on disease progression and improve prognosis.
