Clinical and pathogenetic insights into Herpes zoster duplex.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.34.3.2659How to Cite
Abstract
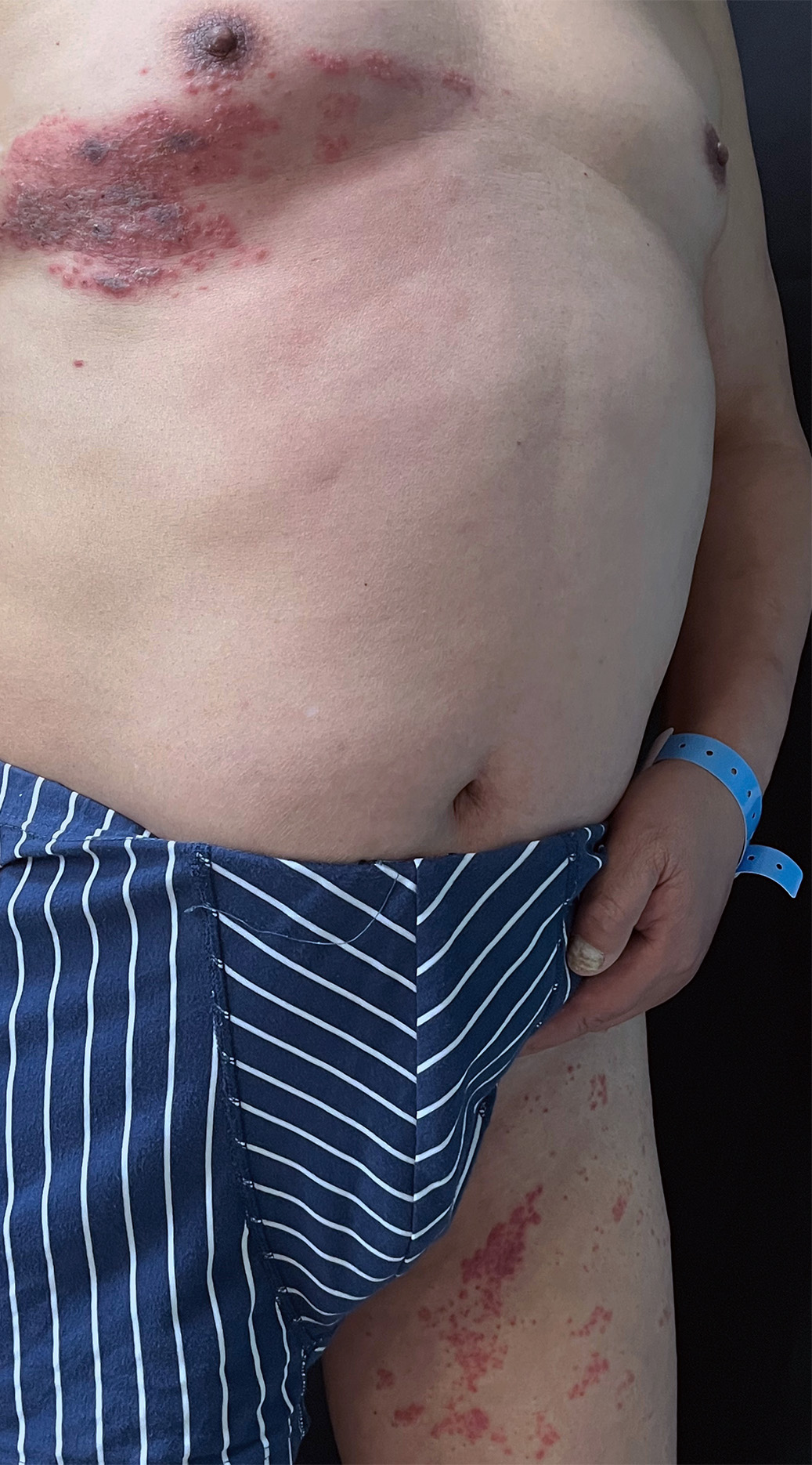
Herpes zoster (HZ) is a frequent dermatitis caused by reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), previously silent in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord after primary infection. It is more common in adults and the elderly and occasional in children. HZ affecting two dermatomes or HZ duplex (HZD), has a clinical incidence of less than 0.5% and is typically related to an impaired immune response. In particular, it is frequently observed in individuals with malignancies, diabetes, prolonged chemotherapy or radiation therapy, high-dose corticosteroid use, and prolonged immunosuppressive therapy. In the current report, 4 cases of HZD are presented in patients immunosuppressed due to other diseases, its pathogenesis is discussed and its risk factors are analyzed, in order to stimulate greater vigilance among dermatologists who manage immunocompromised patients.
