Clinical aspects and SCORing MAstocytosis (SCORMA) index assessment in cutaneous mastocytosis in 36 pediatric patients.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.33.1.2451How to Cite
Abstract
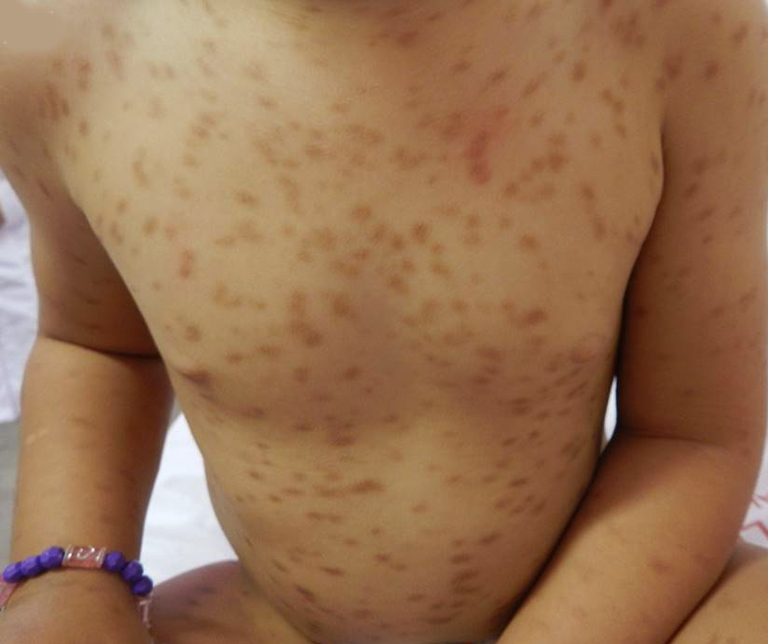
Objective. To determine the clinical characteristics and assess the severity of pediatric patients with mastocytosis using SCORing MAstocytosis (SCORMA) index.
Methods. Observational and descriptive study, with ambispective data collection. Over the past ten years, medical records were reviewed at a referral center for a total of 36 cases, and SCORMA was prospectively applied to 16 patients. The data were evaluated with the JMP10® program through Pearson’s chi-squared test and Mann Whitney’s test, considering a significance level of 5%.
Results. 36 children under 18 were included. Twenty-one patients had maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis, 14 patients had mastocytoma, and 1 had diffuse cutaneous mastocytosis. Symptoms, mainly itching and abdominal pain, were present in 25 patients (70%). The SCORMA index had a median of 34 (range 10.2 to 65.5) and was higher in symptomatic than in asymptomatic patients (p=0.01).
Conclusions. Maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis is the most frequent form, often symptomatic and the SCORMA index has made it possible to objectively evaluate the severity of the disease, proving to be a valuable tool for outpatient follow-up.
