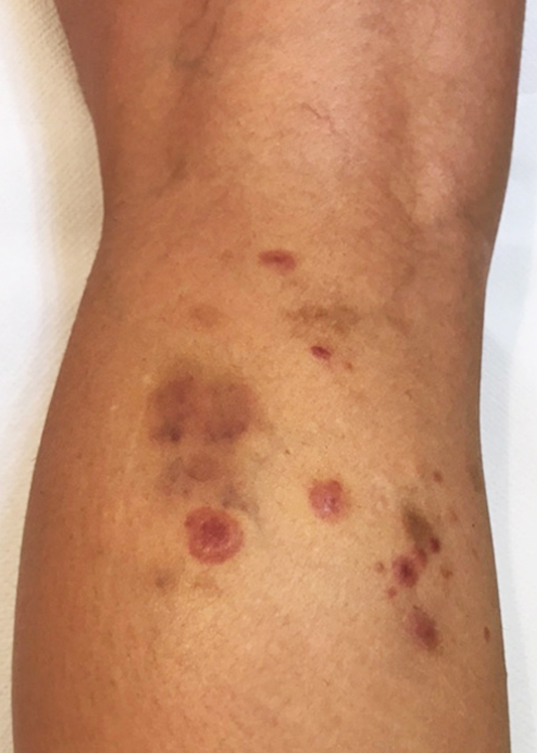
Localized type A lymphomatoid papulosis.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.32.1.2326How to Cite
Abstract
In the WHO-EORTC classification (9), lymphomatoid papulosis (LP) is included among the primary cutaneous lymphomas (PCLs), that is, non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas which do not present extracutaneous manifestations at the time of diagnosis. PCLs have a significantly different clinical behavior from lymph node lymphomas that secondly affect the skin, because PCLs remain confined to the skin for a long time or forever and often regress spontaneously. PCLs include both T-cell lymphomas which make up 80% and B-cell lymphomas. T-cell PCLs, consisting of residential skin T cells, include mycosis fungoides, which accounts for 60% of cases and at the second place for frequency – 25% of cases – the so-called CD30 + lymphoproliferative disorders (9). The latter include LP and CD30+ anaplastic, large cell lymphoma, which represent parts of the same disease spectrum, are not histologically distinguishable and differ essentially because the skin lesions in lymphoma do not heal spontaneously unlike those in LP.
