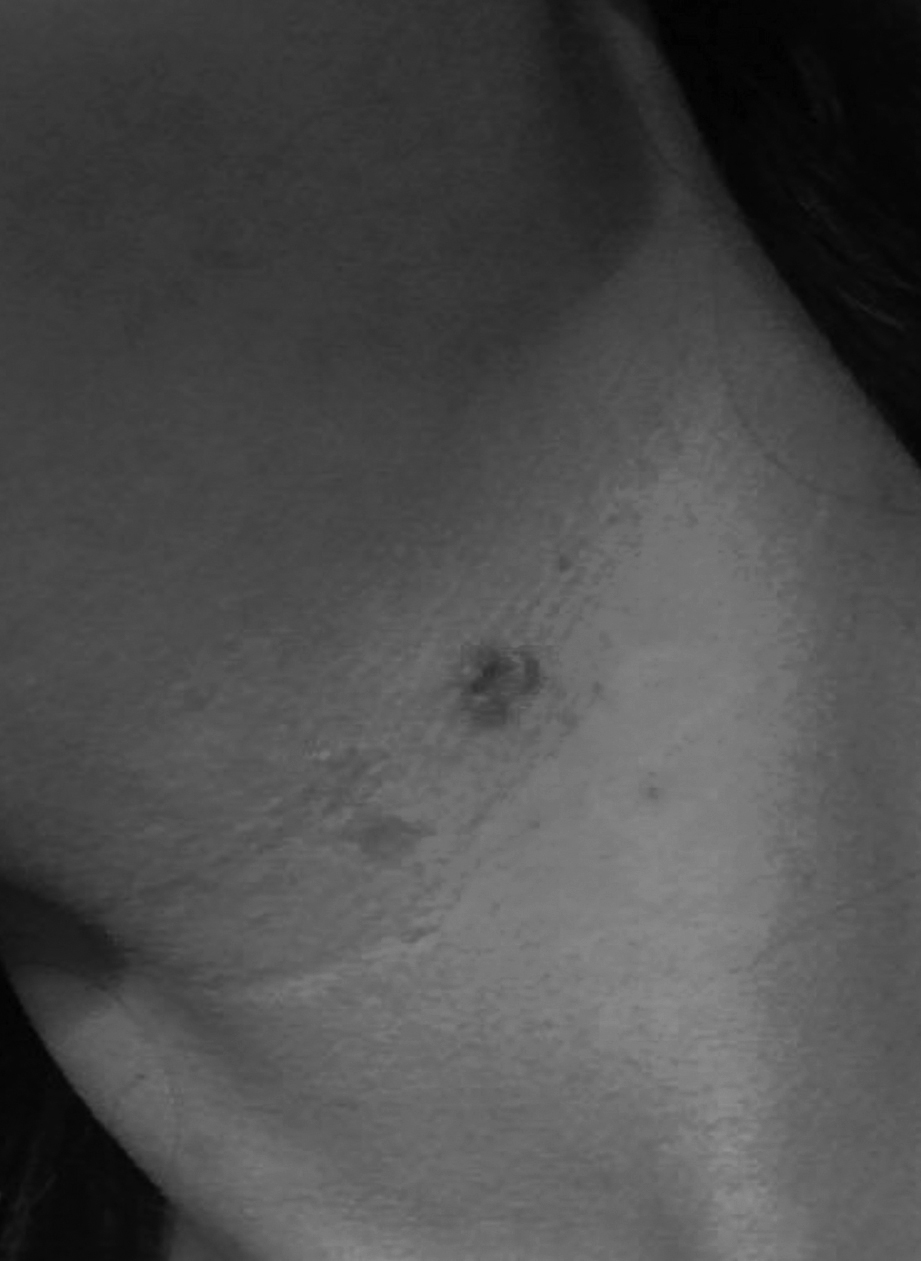
A rare side effect of D-Penicillamine therapy: elastosis perforans serpiginosa.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.29.2.1968How to Cite
Abstract
Elastosis Perforans Serpiginosa (EPS) is a rare perforating skin disorder. EPS can be idiopathic, reactive or drug induced. Here was reported a case of an adolescent affected by Wilson’s disease and treated with D-penicillamine for the last 11 years, who presented with multiple reddish keratinized papules coalescing in the anterior region of the neck. This finding was found to be typical D-Penicillamine induced EPS. The lesion biopsy showed transepidermal perforation due to elastotic material and inflammatory dermal infiltrate of lymphocytes and plasma cells with multinucleated giant cells. The previous therapy was changed to oral zync. It is estimated that EPS occurs in only 1% of patient treated with D-Penicillamine. The latter is the only drug capable of inducing EPS.
