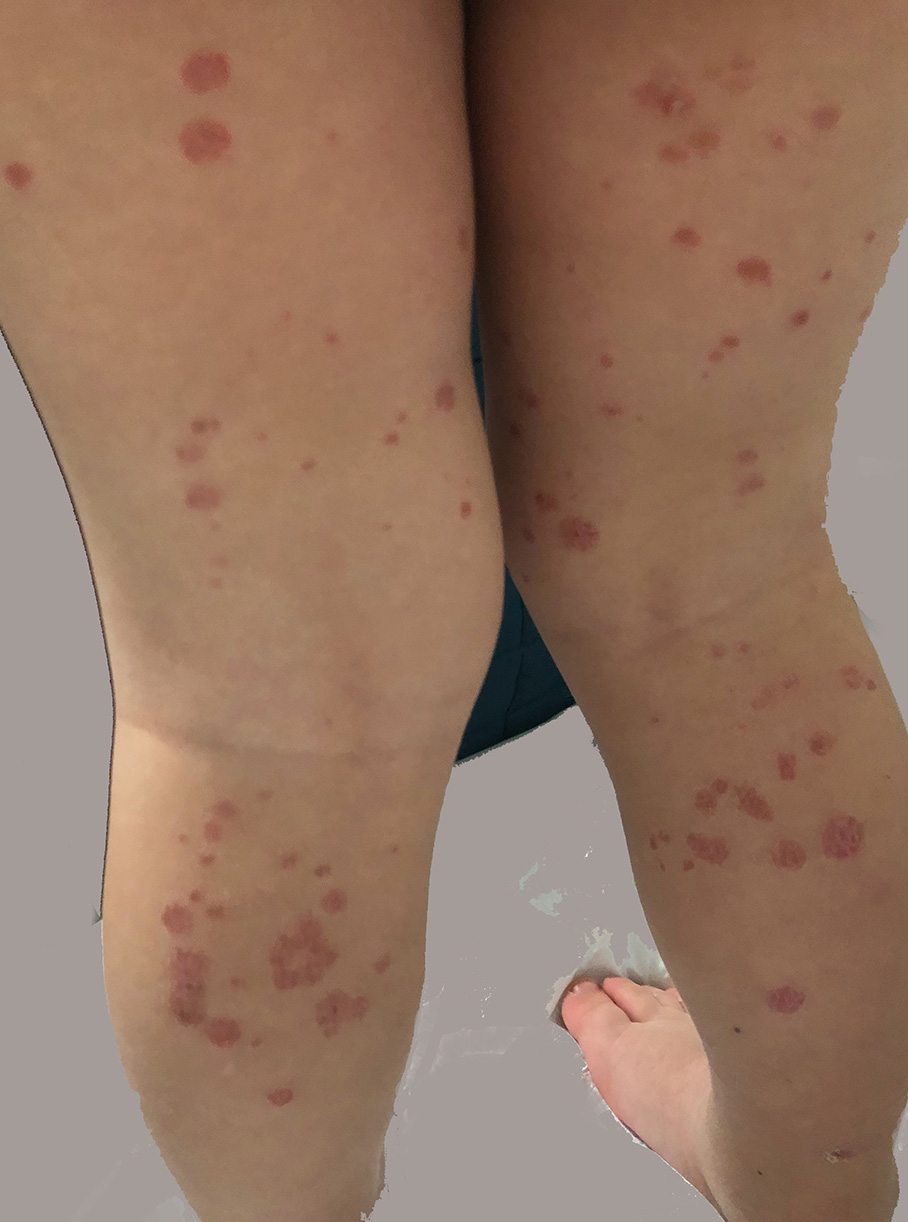
Guttate psoriasis post-hand, foot and mouth disease.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.29.1.1954How to Cite
Abstract
We have not found in the literature cases of guttate psoriasis secondary to hand, foot and mouth disease.
The only report in the literature on the relationship between psoriasis and hand, foot and mouth disease is a case of plaque psoriasis in an adult patient who developed hand, foot and mouth disease after the infection of the daughter. This patient showed an elective concentration of vesicular and pustular lesions on the psoriasis plaques; this localization was attributable to the vasodilatation induced by psoriasis similarly to what occurs in eczema coxsackium.
Guttate psoriasis is sometimes caused by a group A beta-haemolytic streptococcus infection. However, in dermatology it is not exceptional that the same cutaneous manifestation, for example erythema multiforme, may be caused by both a viral infection and more rarely a bacterial infection.
