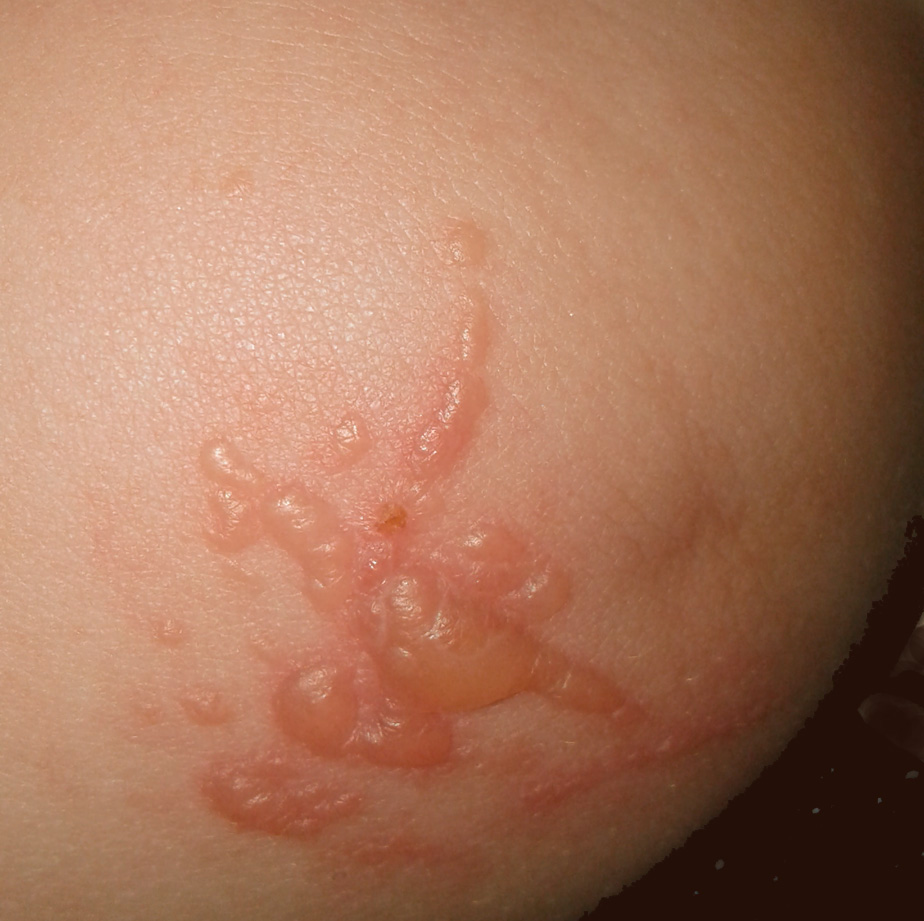
Junctional, localized epidermolysis bullosa mitis (non Herlitz) associated with a new ITGB4 mutation.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.28.4.1924How to Cite
Abstract
(...) Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (EB) traditionally divides into a severe form (Herlitz) and a mild generalized form (non-Herlitz). Both forms are transmitted in an autosomal recessive manner. The disorders are characterized ultrastructurally by a cleavage at the level of the lamina lucida immediately below the plasma membrane of the basal epidermal cells and by evident ultramicroscopic abnormalities of the hemidesmosomes.
Among the variants of junctional EB there is also the form associated with pyloric atresia (PA). While the first two are linked to mutations of the genes codifying for laminin, the junctional EB associated with PA is due to mutations of genes codifying for integrin alfa6 (ITGA6) and beta4 (ITGB4). These integrins are transmembrane proteins expressed electively in the skin, gastrointestinal and urinary tract, which together with the laminin and the plectin ensure the integrity and stability of the anchoring hemidesmosomes. (...)
