Langerhans cell histiocytosis: II - Cutaneous self-healing acquired variety.
Downloads
How to Cite
Abstract
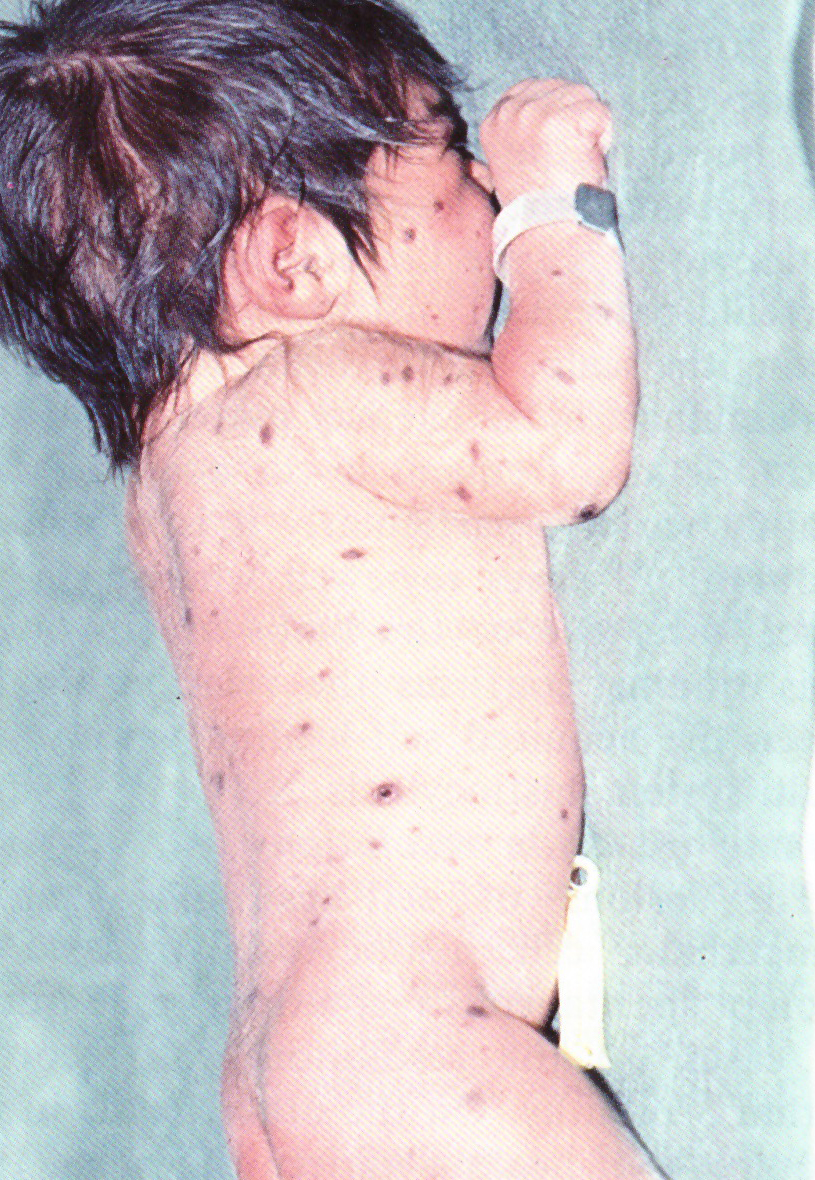
It is well-known today that many cases of Langerhans cell histiocytosis may spontaneously recover without any treatment. Most of these patients present specific lesions at birth. However, in many cases the lesions appear after birth. In this report were reviewed 15 cases (3 personal cases + 12 of the relevant literature) of self-healing acquired Langerhans cell histiocytosis, in arder to put in evidence the possible clinical characteristics able to predict a benign course. The cases were included in this review provided that they satisfied the following 3 criteria: 1- involvement of the skin, 2- absence of lesions at birth, 3- healing without treatment. The clinical features of these patients - sex, age of onset, characteristics of lesions (number, morphology, color, size, purpuric component, residual manifestations), sites involved, timing of resolution of the skin lesions and finally involvement of other organs - were comparatively evaluated with those of 46 cases of self-healing congenital Langerhans cell histiocytosis and 90 cases of histiocytosis X. The comparative evaluation of the clinical features showed that self-healing acquired Langerhans cell histiocytosis is much more similar to histiocytosis X type Letterer-Siwe than the self-healing congenital variety type Hashimoto-Pritzker disease, the only difference being the decreased number of skin lesions and their more prominent monomorphism.
