Skin hyperpigmentation due to anticonvulsant drugs.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.28.1.1659How to Cite
Abstract
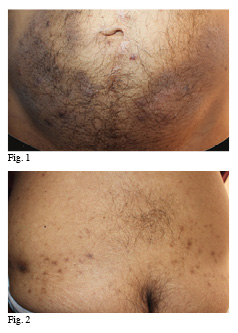
A melanic hyperpigmentation can be due to numerous endogenous and exogenous causes. Limiting ourselves to pharmacological causes only, we should remember (2) that a skin hyperpigmentation may be due to arsenic, chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine and to anticancer drugs such as bleomycin, cyclophosphamide, 5-fluorouracil, methotrexate etc.
Among the neuroleptic drugs the first place belongs to diphenylhydantoin: 10% of patients treated with this drug develop a chloasma-like hyperpigmentation probably due to direct action of the drug on melanocytes. Some patients treated with chlorpromazine for a long time have a blue-gray pigmentation of the photo-exposed areas, probably due to the formation of melanin-chlorpromazine complexes that are not metabolized by the body. A case of levetiracetam hyperpigmentation has also been described (1).
