VESICLES. III. Atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, pompholyx, sudamina.
Downloads
How to Cite
Abstract
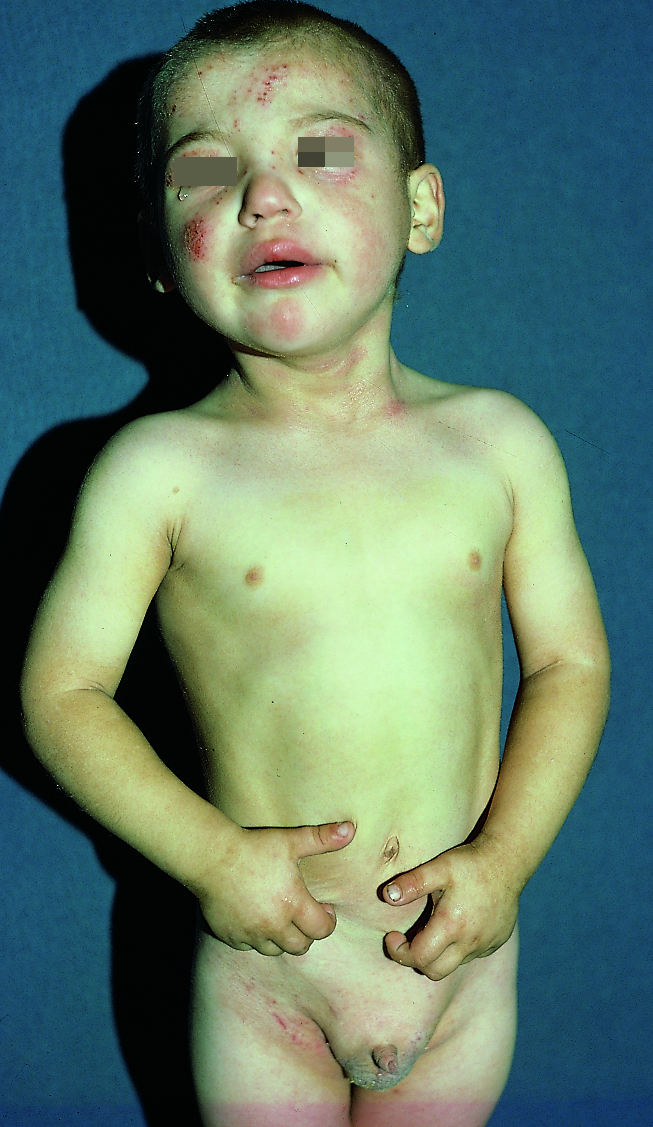
AD "sine" AD. The forms of AD with intense itching and few or absent spontaneous lesions (Fig. 529) belong to this group. The differential diagnosis of these forms is easy as the other intensely itchy dermatoses, notably scabies, hypersensitivity to mosquito bite and dermatitis herpetiformis, are always associated with spontaneous lesions. An exceptional event in childhood is the presence of itching determined by other extracutaneous diseases, such as neoplasms.
The role of the atopic constitution in the development of this form of AD is confirmed by the familial and personal history of atopy, the seasonal course of itching, which disappears in summer and deteriorates in spring and autumn, and the demonstration of specific IgE for environmental substances in both the skin and serum of these children. (...).
