Difficulties in the diagnosis of sporadic multiple trichoepitheliomas.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.27.4.1518How to Cite
Abstract
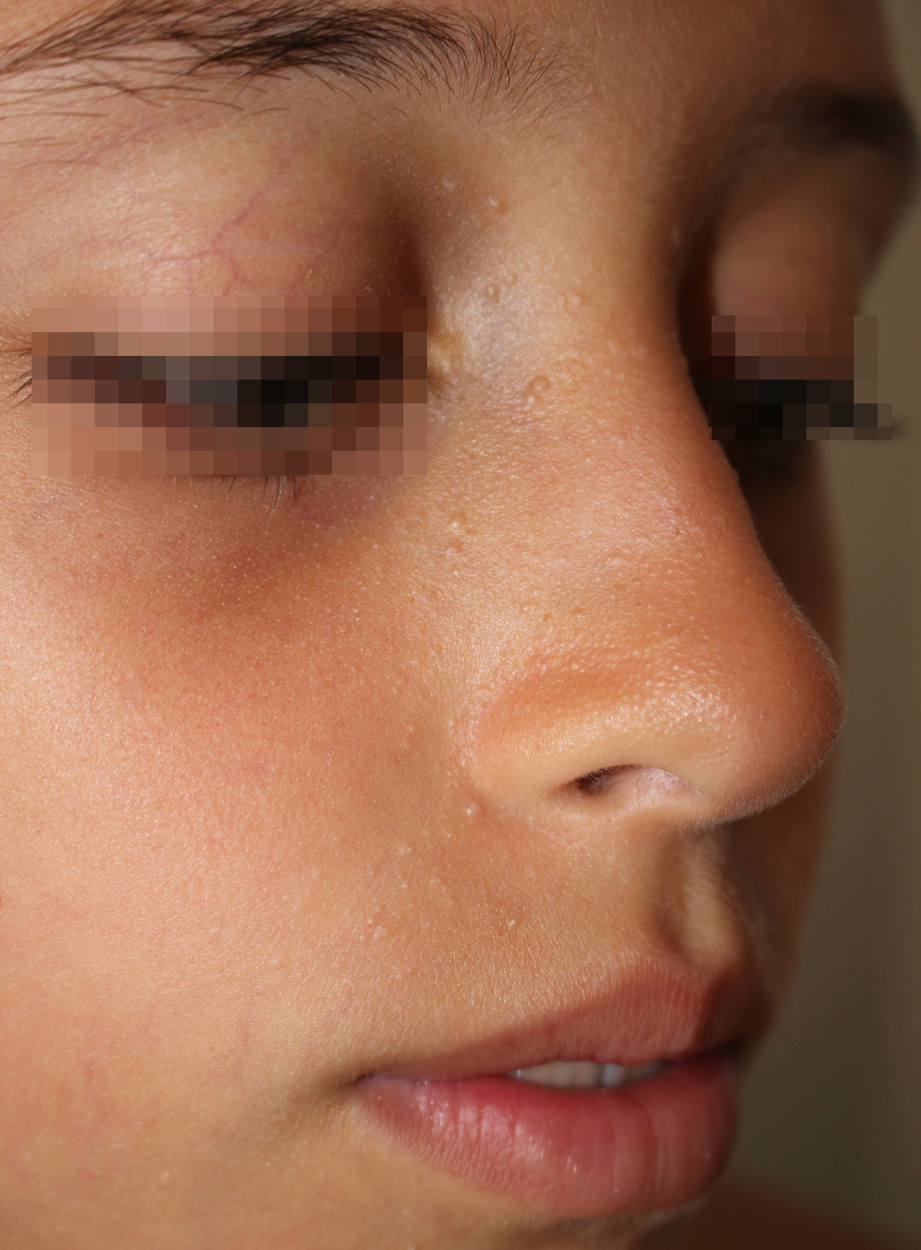
Multiple trichoepitheliomas can present some diagnostic difficulties both from a clinical and histological point of view. From a clinical point of view the differential diagnosis in the child should be made with molluscum contagiosum, flat warts, angiofibromas of tuberous sclerosis, follicular keratosis and milia. Molluscum contagiosum can be located around the nose, but it is rarely bilateral and symmetrical from the beginning. With time, some elements of molluscum contagiosum often regress sometimes through an inflammatory phase; moreover, the larger elements have a characteristic central depression. According to some Authors (1, 4), this depression can be seen earlier in the smaller elements thanks to the dermoscope. On the other hand, trichoepithelioma would be characterized dermoscopically (5) by arborizing vessels, milium-like cysts and rosettes on a whitish background; however, in our case we saw with the dermoscope only a whitish non-vascularized amorphous mass. Flat warts, besides the infectious-type distribution in common with molluscum contagiosum, that is at least initially asymmetric with elements of different sizes, have a flat surface and an opaque appearance. The angiofibromas of tuberous sclerosis at least initially can simulate trichoepitheliomas both for distribution, size and appearance; however, they increase in number in less time and at least some of them have a typical reddish color linked to the angiomatous component (2). Follicular keratosis affects the lateral regions of the face and the extensor surface of the arms, improves in the summer, gives a sensation of rasp to the touch and the lesions are pointed (3). Milia, which are the most similar lesions to trichoepitheliomas, affect the lower eyelids and the cheeks and are more whitish in color.
From a histological point of view the differential diagnosis should be made from basal cell carcinoma: in trichoepithelioma the tumor aggregates are never in connection with the epidermis and are not surrounded by artificial fissures, there is a tendency to follicular differentiation, the stroma surrounding the cellular aggregates recalls the mesenchymal papillary bodies and contains fissures.
