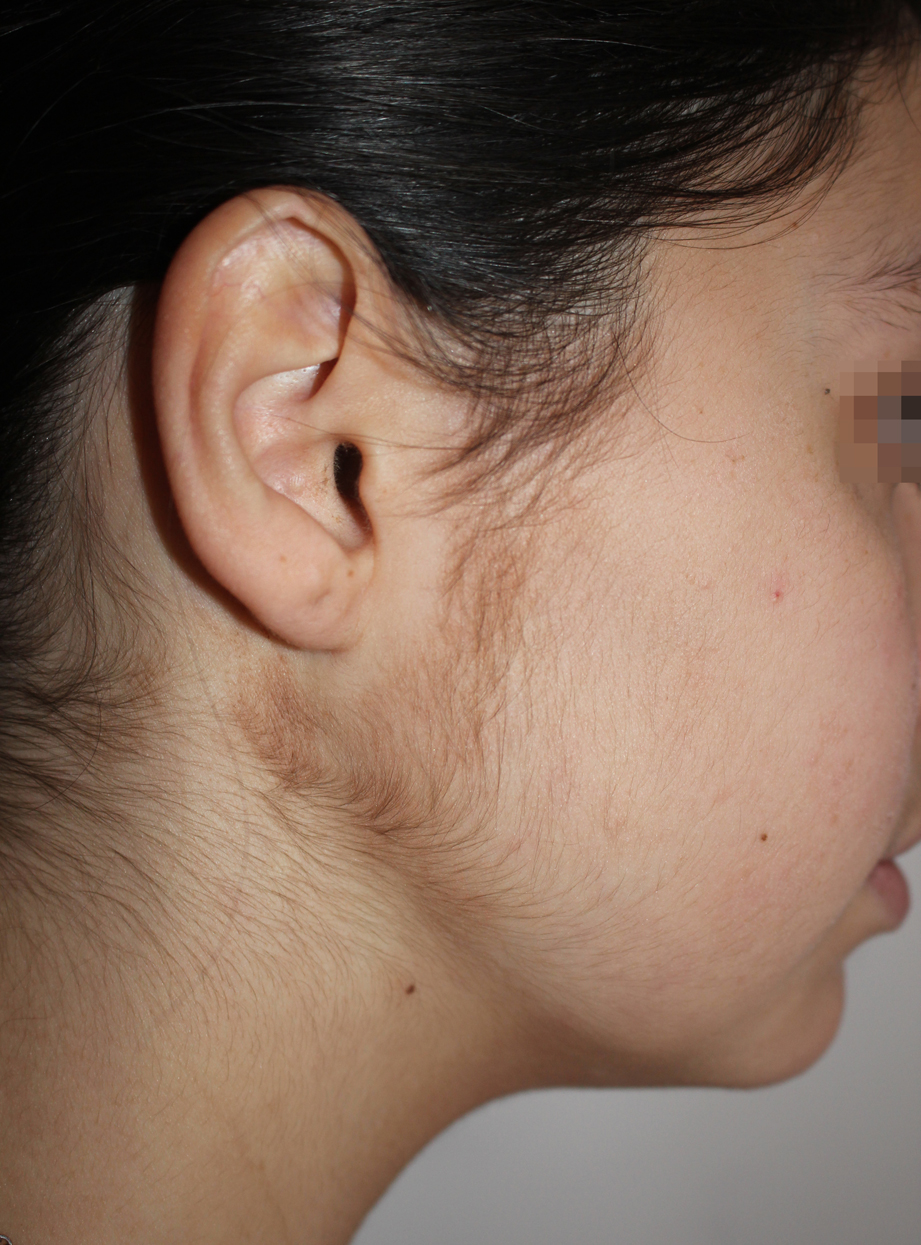
Terra firma dermatosis in patient treated with vedolizumab.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.27.4.1509How to Cite
Abstract
Vedolizumab is a humanized monoclonal IgG1 antibody produced from Chinese hamster ovary cells. The antibody binds specifically to α4β7 integrin, which is electively expressed on intestinal helper T cells. By binding to integrin α4β7 vedolizumab inhibits the adhesion of lymphocytes to the mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule (MAdCAM-1) expressed mainly on endothelial cells of the intestine. For this reason the monoclonal antibody vedolizumab is a biological immunosuppressant with selectivity for the intestine and is therefore indicated in Crohn’s disease and in ulcerative colitis. Eczematous dermatitis is described as a common side effect of vedolizumab; also terra firma dermatosis could be attributed to vedolizumab since it has never been described in association with the very frequent oral corticosteroid therapy; the latter could be responsible for hypertrichosis.
