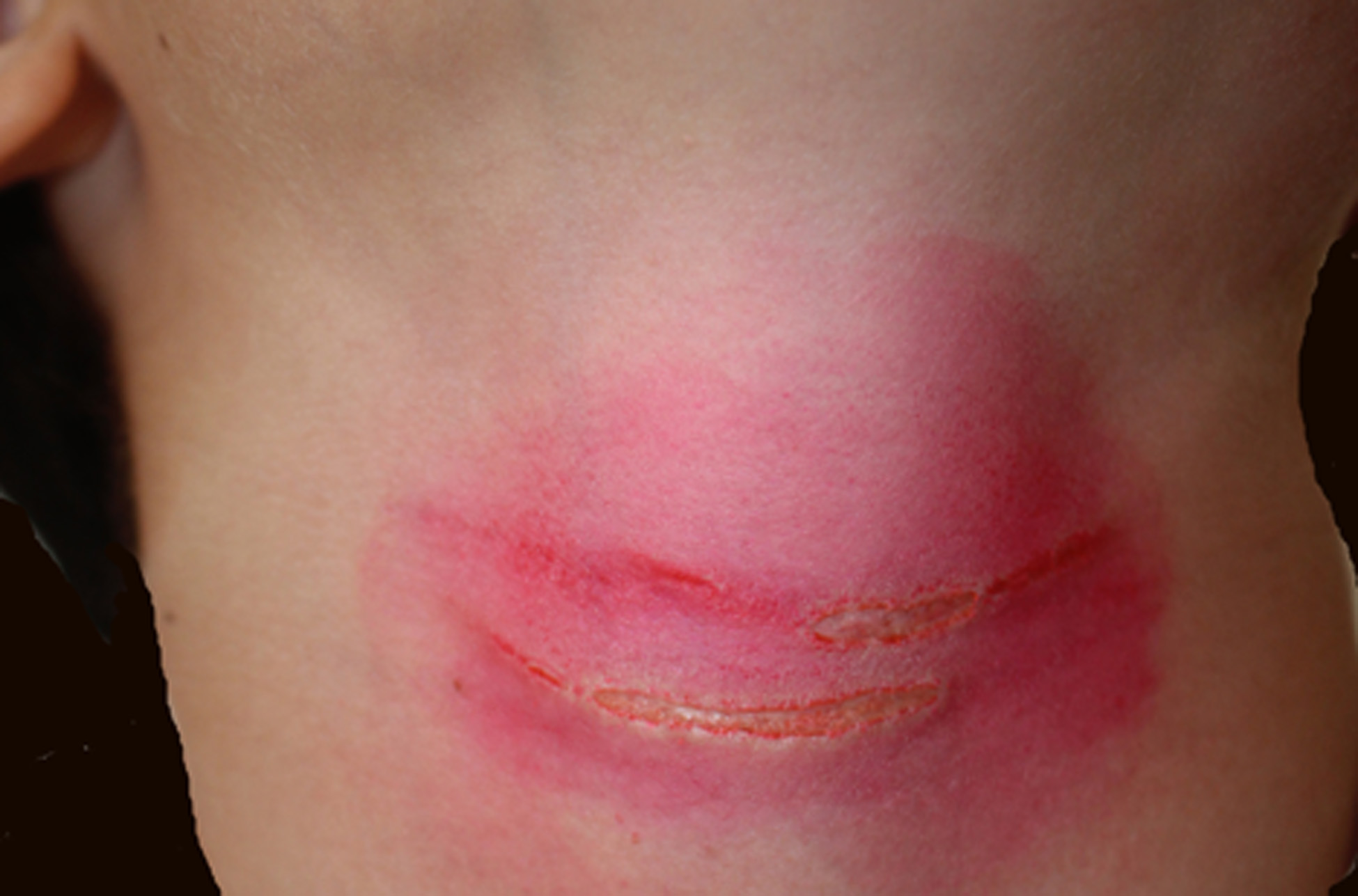
Irritant contact dermatitis due to jellyfish.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.27.4.1508How to Cite
Abstract
The jellyfish (philum Cnidaria) present in their tentacles many nematocists, i.e. cells containing irritant substances, useful both for defense and capturing prey.
The irritant substances are released from a filament usually spirally coiled inside the cell that can be quickly uncoiled and everted.
In most cases, irritant contact dermatitis ranges from erythema to necrosis and is responsible for intense subjective symptoms (2).
In some cases there may be local reactions of allergic contact dermatitis and general reactions that may, however, rarely cause exitus. After contact with a jellyfish, the baby must go out of the water and any tentacles should be removed from the skin with sea water.
The burning sensation can be attenuated with cold packs (1); anti-inflammatory corticosteroid lotions can also be used.
