Oro-facial granulomatosis
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.27.3.1475How to Cite
Abstract
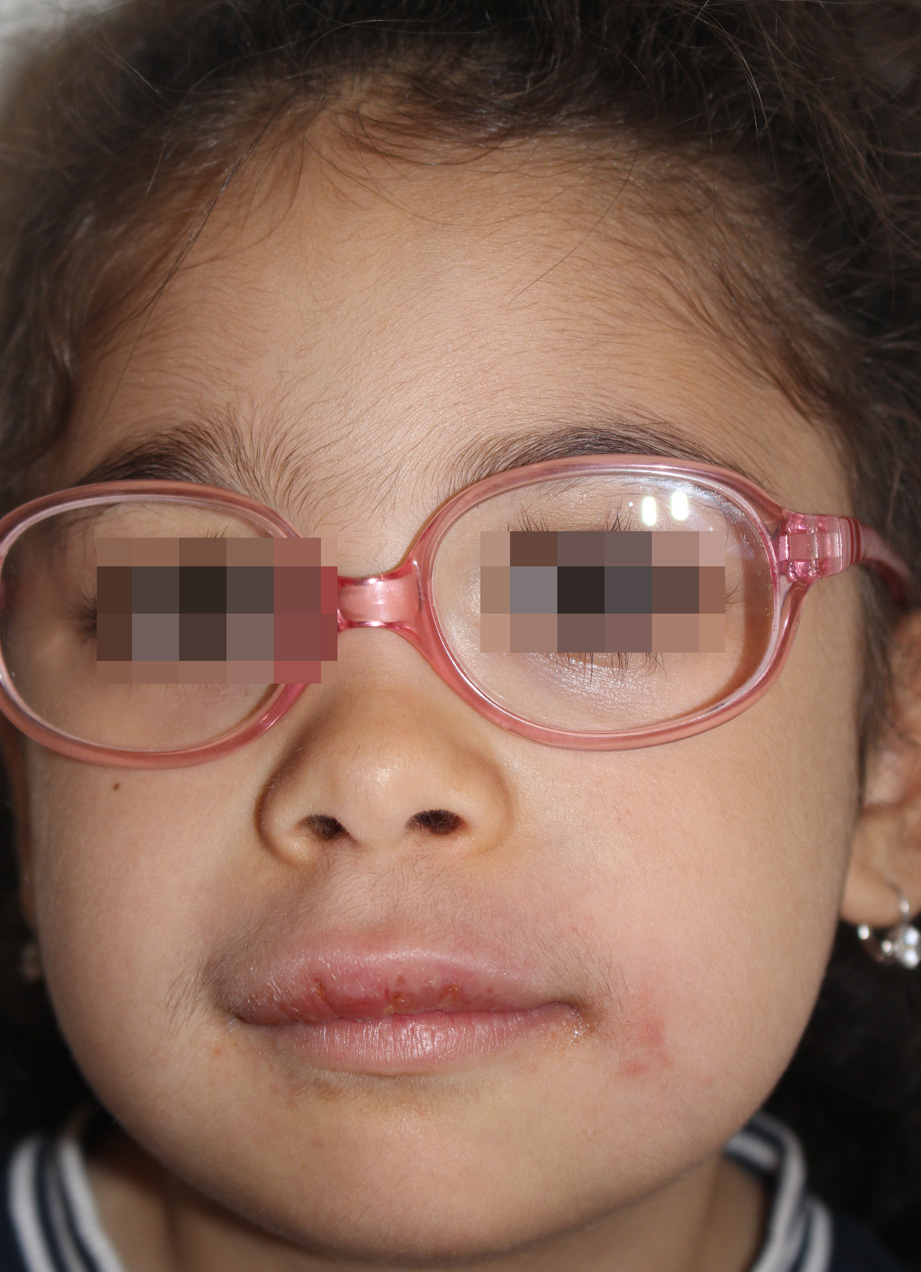
Oro-facial granulomatosis is clinically characterized by edema initially of short duration and self-healing, but later persistent with phases of transient worsening, affecting the face, mainly the lip.
Histologically, edema of the dermis, lymphangiectasias and lymphocyte infiltration initially, then followed by giant cell granuloma can be observed. From the etiologic point of view, the disorder is believed to be due to an exaggerated inflammatory reaction against different exogenous factors in genetically predisposed subjects. In most cases no cause can be highlighted, but the overlap of clinical and histological findings with Crohn’s disease and the possible subsequent appearance of this disease has led to hypothesize that oro-facial granulomatosis could represent a
mild, sometimes only cutaneous form of Crohn’s disease.
