Atopy patch test and specific IgE against chicken egg white and egg yolk in atopic dermatitis pediatric patients with a history of chicken egg allergy
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.27.3.1450How to Cite
Abstract
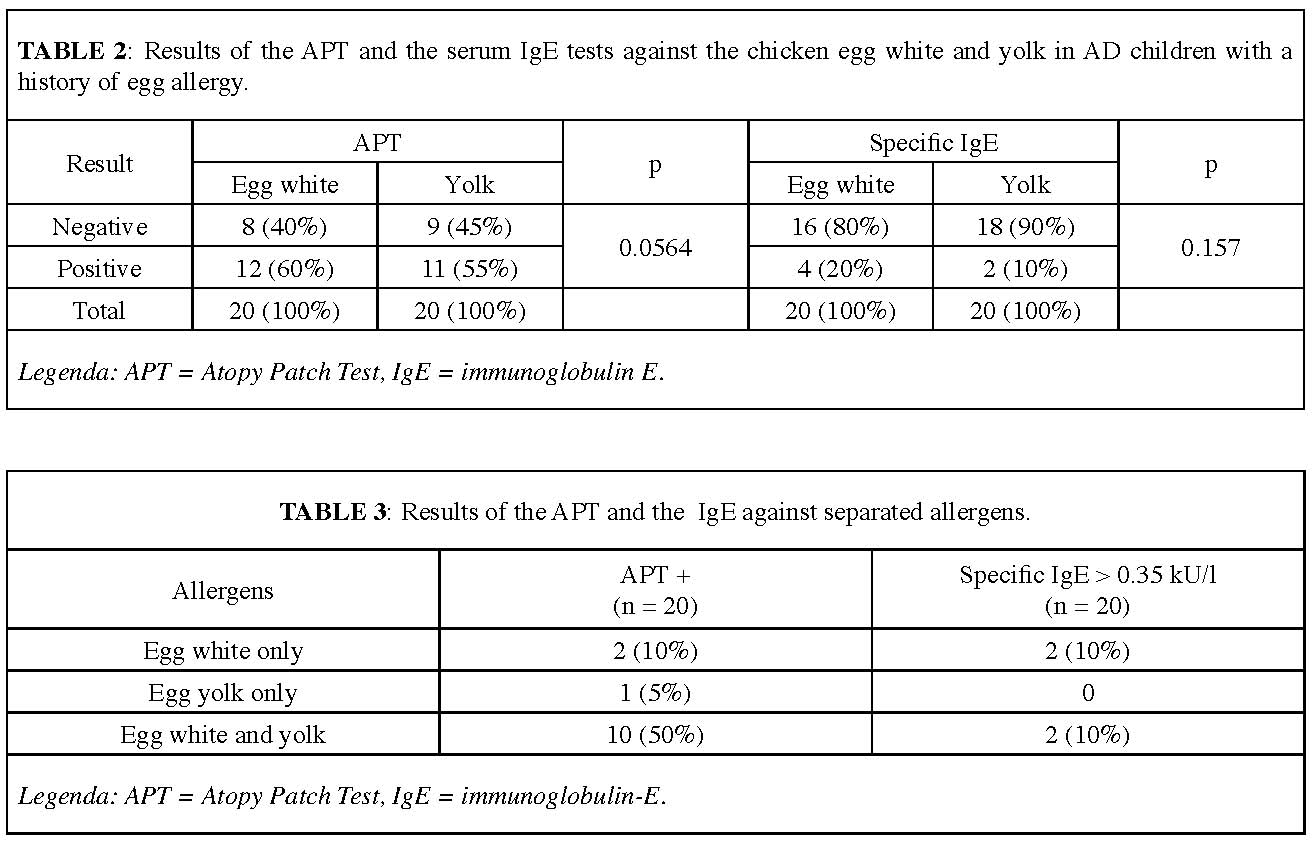
Chicken eggs are one of the food allergens in children. Chicken eggs are contained in many foods; people consume eggs without separating the egg white and the egg yolk. Separating allergens in egg white and egg yolk through an allergy test is expected to specifically determine which allergen can cause allergies. This study determined the profile of Atopy Patch Test (APT) and specific IgE against chicken egg white and egg yolk in 20 atopic dermatitis patients with a history of chicken egg allergy. 2/20 subjects showed positive atopy patch tests against chicken egg white only, 1/20 subject was positive against egg yolk only, and 10 subjects (50%) were APT positive against both chicken egg white and yolk. Meanwhile, based on the value of the specific IgE, 2 subjects (10%) experienced an increase of the specific IgE against egg white only and 2 subjects experienced an increase of the specific IgE against both egg white and yolk. By separating allergens in both APT and serum specific IgE, the results obtained can be more vivid. These results may be used to educate patients who might be allergic to one of the allergens of chicken eggs.
